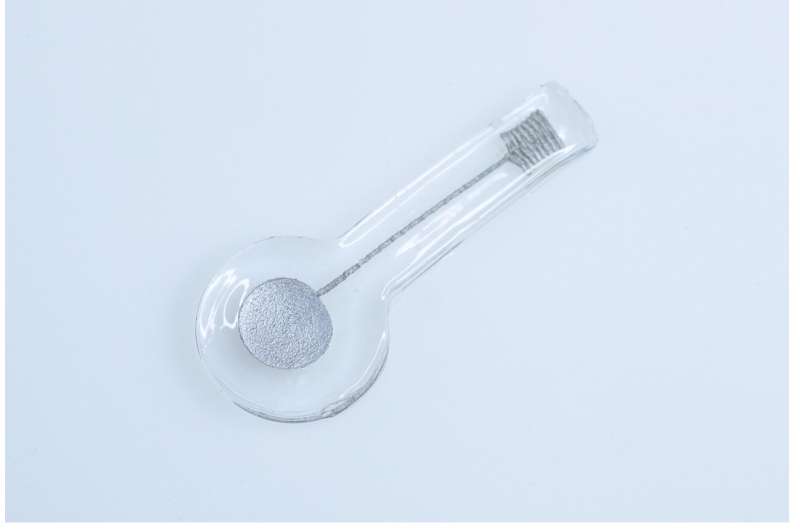
Hydrogels are three-d (3-D) polymer networks that don’t dissolve in water however retain vast quantities of liquids. Because of this positive belongings, hydrogels are in particular promising subject matter platforms for each biomedical and environmental programs, as they may be able to live on in physically fluids or in rainy herbal environments with out dissipating.
During the last decade, engineers and fabrics scientists had been growing a lot of digital units in line with comfortable hydrogels, together with environmental and biomedical sensors, drug supply units, and synthetic tissue. In spite of the massive attainable of those hydrogel-based units, their common implementation has to this point been hindered by means of their top manufacturing prices.
A analysis crew led by means of Dr. Nanjia Zhou at Westlake College and Westlake Institute of Complicated Research in China have lately offered a brand new approach to allow the 3-D printing of soppy hydrogel electronics. Their technique, offered in a paper revealed in Nature Electronics, may lend a hand to decrease the manufacturing prices of a lot of hydrogel-based units, together with pressure sensors, inductors, and organic electrodes.

“We select to check hydrogel manufacturing as a result of whilst lots of the present comfortable electronics are in line with versatile elastomers and polymers, undeniably hydrogel is extra very similar to the human frame and might result in higher tissue integration and not more immune responses,” Dr. Yue Hui, one of the vital researchers who performed the find out about, advised TechXplore. “As steered by means of in the past research, we expect that hydrogel is a promising candidate for the advent of long term well being care digital units.”
The essentially purpose of the new find out about by means of Hui and his colleagues was once to plot an effective approach to fabricate more and more advanced and biomedically helpful hydrogel-based electronics. Their proposed technique is in line with 3-D printing generation, in particular using a hydrogel-based supporting matrix and a stretchable silver-hydrogel ink.
“The embedded 3-D printing approach we advanced comes to the freeform printing of a conductive hydrogel ink right into a hydrogel supporting matrix, and the following curing of the 2 portions to shape a comfortable and stretchable digital instrument,” Hui defined. “Those are in line with the appropriate rheological homes of the matrix and the ink, in addition to the orthogonal curing mechanism of alginate and polyacrylamide, which can be the primary parts of the hydrogel.”
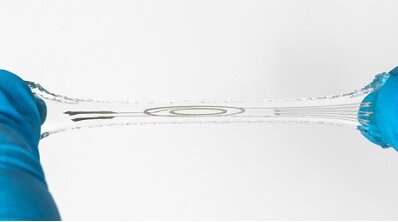
The researchers discovered that combining a conductive filler (i.e., silver flakes) with granular gel debris ended in the formation of a segregated construction within the conductive 3-D printing ink. This ink exhibited a exceptional electric conductivity of over 1,400 S/cm.
To exhibit the feasibility in their proposed technique, Hui and his colleagues used it to create a sequence of hydrogel-based electronics, together with pressure sensors, inductors and organic electrodes. The ensuing units have been discovered to accomplish exceptionally neatly, suggesting that this technique might be used to create a spread of latest hydrogel-based applied sciences.
“As we exhibit in our paper, our approach can be utilized to make more than a few hydrogel digital units with other functionalities,” Hui stated. “Specifically, we will be able to immediately print uncovered electrodes that may keep up a correspondence with the outdoor international, and we will be able to incorporate parts corresponding to LEDs and chips into the circuitry by the use of printing. Our findings indicate that with subtle design we will be able to truly make practical hydrogel digital units.”
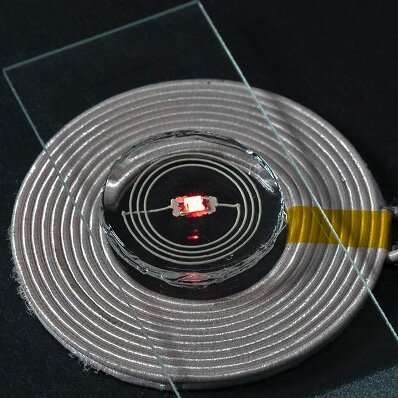
Someday, the new paintings by means of this crew of researchers may allow the fabrication of extra advanced and complicated hydrogel-based electronics, together with biomedical units and new applied sciences to watch the surroundings. Hui and his colleagues are actually running to make stronger their 3-D printing approach to additional facilitate its real-world and large-scale implementation.
“We can now stay optimizing the fabrics and strategies,” Hui added. “As an example, a scientific and theoretical find out about in regards to the conductive ink with segregated construction remains to be missing, that may be the important thing to additional make stronger its conductivity. We additionally plan to design and fabricate biomedical units and validate their functionalities in animals.”
Additional information:
Yue Hui et al, Third-dimensional printing of soppy hydrogel electronics, Nature Electronics (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41928-022-00887-8
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
A brand new technique for the 3-D printing of hydrogel-based electronics (2023, January 10)
retrieved 23 February 2023
from https://techxplore.com/information/2023-01-approach-3d-hydrogel-based-electronics.html
This file is topic to copyright. With the exception of any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions most effective.
Supply By way of https://techxplore.com/information/2023-01-approach-3d-hydrogel-based-electronics.html