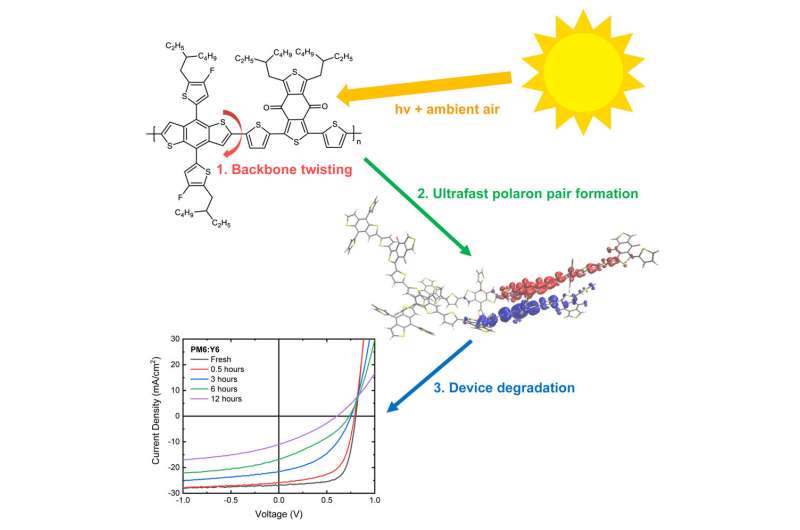
Our society has a love affair with plastic. To take our dating to the following stage—luckily ever after in a waste-free long term—the trail is round.
In particular, scientists on the U.S. Division of Power’s (DOE) Argonne Nationwide Laboratory are running to investigate the affect of a round economic system the place plastics are reproduced, reused or recycled to stop them from finishing up in landfills.
However get there? Plastics have historically been produced thru a linear take-make-waste type the place plastics are disposed after one use. The problem is discovering an efficient pathway through which plastic by no means turns into waste—the objective of a round economic system.
A round manner considers all the lifecycle of a product, together with end-of-life remedy, on the time of design. Assets in waste streams are reused on the best stage to steer clear of waste and cut back environmental affect. Nonetheless more difficult is discovering an manner that holistically evaluates manufacturing, use and reuse of plastic.
In step with round pondering, Argonne scientists created a sustainability research framework to guage more than a few round economic system methods for inspecting sustainability affects of manufacturing, use and remanufacturing for reuse of plastic.
“The long-term sustainability of our planet calls for a significant shift from a linear economic system, the place items are discarded after use, to a round economic system of restoration, recycling and reuse,” mentioned Troy Hawkins, chief of Argonne’s Fuels and Chemical compounds Team. “Many merchandise with recyclable content material are these days despatched for disposal.”
Of their analysis, scientists used polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a plastic used widely in bottles, for example to use the round modeling framework. PET is a mild, sturdy plastic maximum steadily utilized in bottled water and comfortable beverages.
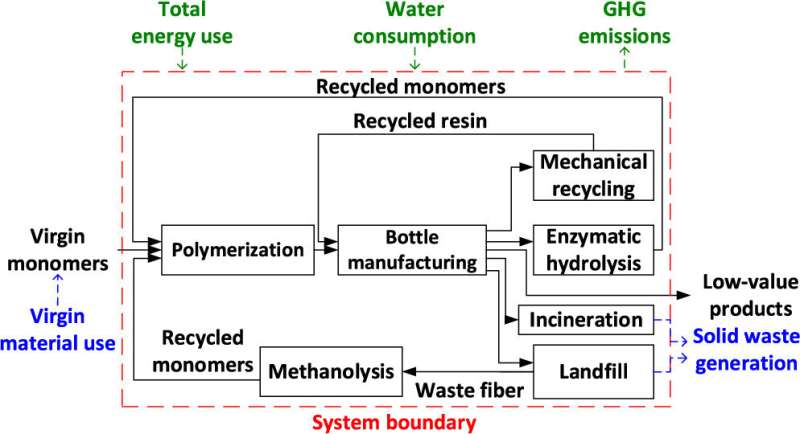
Argonne’s complete research framework for round economic system sustainability combines life-cycle research (LCA) with subject material glide research. This new manner supplies an review of the environmental affect of PET bottles over all the lifestyles cycle.
The brand new analysis is revealed in revealed in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
What’s the procedure?
Of their research, researchers factored in detailed life-cycle metrics of all phases of plastics recycling.
They included information for getting better, sorting and keeping apart precious subject material for recycling, which is changing into more and more complicated because of the sheer choice of plastics and huge array of makes use of. Through doing this, researchers have been in a position to supply reasonable eventualities and effects.
Researchers analyzed more than a few pathways for understanding a round economic system. In a single state of affairs, they analyzed provide chain inputs of 2 standard routes for generating plastic, in addition to mechanical and chemical recycling.
Mechanical recycling is the commonest recycling procedure however has drawbacks. The method recovers plastic via sorting, cleansing, grinding, re-granulating and compounding. Each and every time plastic is recycled this fashion, its high quality is degraded. The brand new, decrease grade plastic may also be recycled an overly restricted choice of instances ahead of it turns into too degraded to make use of.
In a way, chemical recycling selections up the place mechanical recycling leaves off. An rising generation, chemical recycling breaks plastic right down to its unique elements, developing high-grade subject material that may be upcycled, or reworked right into a product of upper worth. On this approach, chemical recycling can be utilized to upcycle waste now not appropriate for mechanical recycling.
Each and every has benefits and drawbacks. Mechanical recycling has a smaller carbon footprint. As a more recent generation, chemical recycling is dearer, and its power use and greenhouse fuel (GHG) emissions is analogous to new plastic.
What are the consequences?
Within the learn about, scientists sought to resolve how mechanical and recycling paintings in combination.
In a single state of affairs, researchers explored the mixing of mechanical and chemical recycling within the provide chain. They made up our minds that whilst integrating mechanical and chemical recycling didn’t lower or build up GHG emissions, the forged waste technology was once lowered via 44% in comparison to the present apply.
Researchers discovered that any given round pathway can produce air pollution and local weather affects that do not occur in parallel. For instance, a pathway the use of mechanical recycling would possibly cut back GHG emissions, however build up dependence on new plastic because of decrease recycling charges.
“We made up our minds there is also tradeoffs between making improvements to circularity and decreasing different environmental affects similar to greenhouse fuel emissions or water intake,” mentioned lead creator Gracida Alvarez.
For instance, expanding the proportion of robotically recycled bottles lowered GHG emissions via 14% whilst the use of chemical recycling and upcycling didn’t affect GHG emissions in comparison to the present apply. Then again, the use of mechanical recycling lowered cast waste technology via 36% in comparison to the present state, against this with the 44% aid in cast waste technology completed via integrating chemical recycling and upcycling, as discussed within the first state of affairs.
Nonetheless, mechanical, chemical and upcycling will play a important function achieve a round economic system.
“Our research means that as we proceed to support chemical recycling and upcycling to generate decrease greenhouse fuel emissions and water intake, mechanical recycling these days supplies important advantages,” Gracida Alvarez mentioned.
Why is it essential?
Plastic air pollution is likely one of the biggest environmental threats to our planet. Plastics Europe estimates that during 2019 on my own, the worldwide economic system produced 368 million heaps of plastic, which is anticipated to double within the subsequent twenty years. Of the plastic waste generated, handiest 9% is recycled, whilst the remaining leads to landfills or is combusted, in keeping with the U.S. Environmental Coverage Company.
There’s no silver bullet resolution. Hawkins mentioned that the use of all 3 recycling processes in tandem, or cascade recycling, is essential in a round economic system. The cascade manner assists in keeping fabrics in flow on the best stage of high quality, financial and environmental worth so long as conceivable.
He likens the cascade option to a waterfall the place the standard of plastic resin decreases because it cascades thru makes use of within the economic system.
“The highest of the waterfall could be a transparent plastic bottle, adopted via a coloured or opaque plastic container. In flip, this bottle may well be recycled right into a polyester fiber and used to provide clothes or carpet,” Hawkins mentioned. “If fiber is the ground of the waterfall, we will use chemical recycling to convey the fabric again to the highest.”
Why is collaboration important?
Argonne researchers collaborated carefully with private and non-private sector companions, who equipped information and experience for the mission. The publicly out there type has industry-wide programs, mentioned Hawkins.
“Our stakeholders are occupied with having rigorous and credible research that is helping construct consensus across the relative affects of more than a few round methods,” Hawkins mentioned. “This can be a powerful, constant framework advanced thru development consensus with stakeholders.”
The Argonne framework was once constructed as an expanded model of the Greenhouse gases, Regulated Emissions, and Power use in Applied sciences type.
Additional info:
Ulises R. Gracida-Alvarez et al, Round Financial system Sustainability Research Framework for Plastics: Software for Poly(ethylene Terephthalate) (PET), ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c04626
Quotation:
Scientists level the right way to a sustainable round economic system for plastics (2023, April 19)
retrieved 21 Would possibly 2023
from https://techxplore.com/information/2023-04-scientists-sustainable-circular-economy-plastics.html
This file is topic to copyright. Excluding any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions handiest.
Supply Through https://techxplore.com/information/2023-04-scientists-sustainable-circular-economy-plastics.html